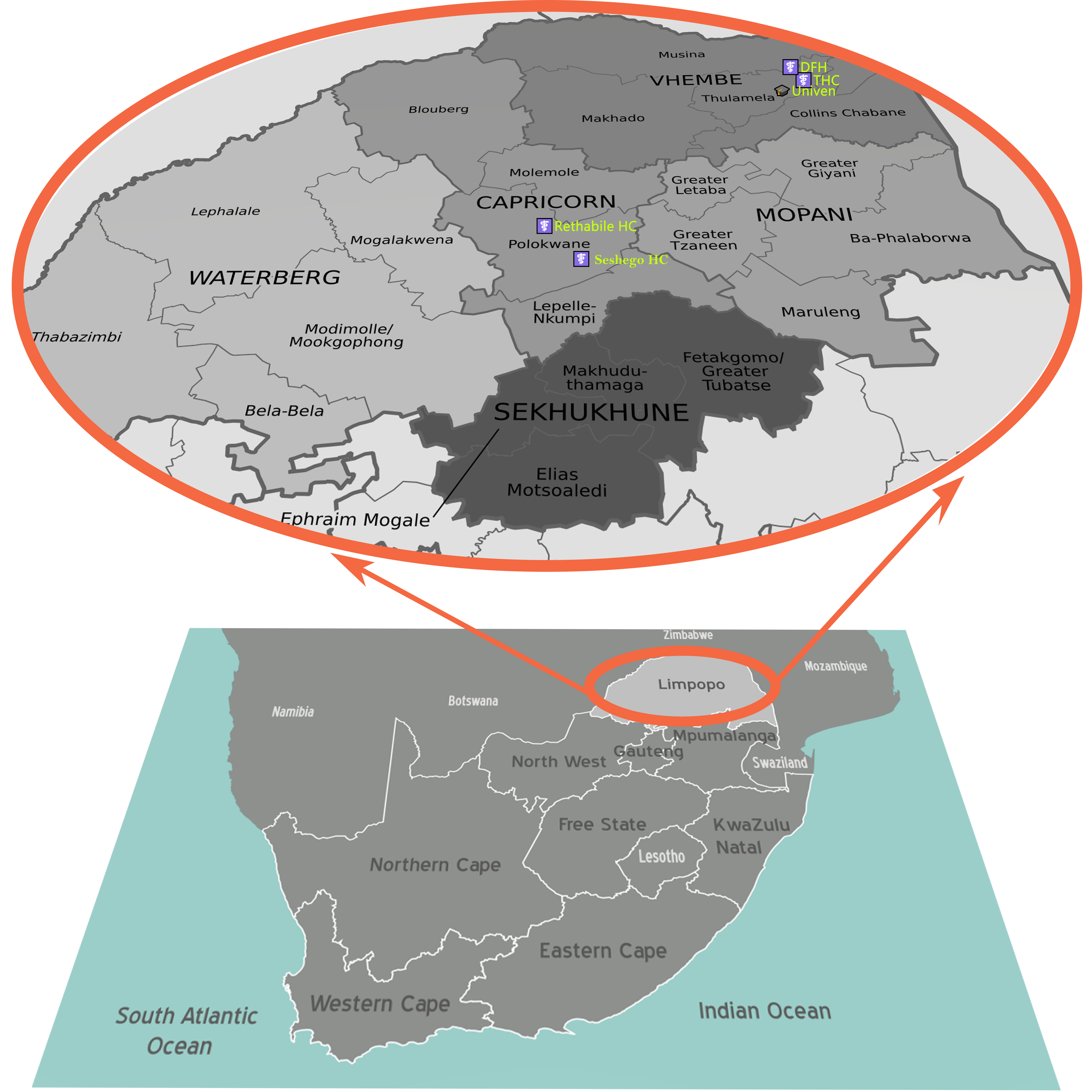
The icons with the red plus sign indicates treatment sites and the graduation cap ontop of stacked books icon indicates the University of Venda
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) diversity in patients intiating treatment in Northern South Africa
Project Aim
The project studied HIV-1 diversity among HIV-1 positive people initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) in Northern South Africa whereby the focus of diversity was on novel HIV-1 variants, pretreatment and acquired drug resistance and treatment outcomes.
Research design
Treatment centers from which participants were recruited
(Leaflet map generated in R)
University icons created by justicon - Flaticon
Hospital icons created by mavadee - Flaticon
Treatment centers from which participants were recruited
(Map generated using QGIS)
Project workflow
The research workflow began with recruiting participants for the study from patients visiting the treatment centers.
Patients interested in participating in the study, were informed about the study, risks, benefits and role they will be playing within the study as a participant. The particants were then requested to sign the informed consent form and shortly after demographic data was collected. Two vials of blood were drawn by a phlebotomist and one vial was transported to a commercial laboratory for viral load testing whereas the second vial as well as the data collected was transported to the University of Venda for CD4+ T cell testing.
The anonymized participant data was captured as well as CD4+ T cell counts and viral load measurements.
This data was used to study treatment outcomes for patients beginning antiretroviral therapy (ART)
Plasma and PBMC (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) was isolated from whole blood. viral ribonuleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was then extracted from plasma and from PBMC respectively.
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and nested PCR were carried out using viral RNA. Nested PCR was carried out from DNA.
Sequencing libraries were prepared for samples successfully amplified and were sequenced using Next generation sequencing (Illumina).
The sequencing reads were then used to pre-treatment and acquired drug resistance and describe novel HIV-1 variant.
The analyzed data was used to draft research reports.